Page 25 - npqh NATIONAL POLICY FOR QUALITY IN HEALTHCARE : Bridging Silos, Accelerating Improvements 2022-2026
P. 25
National Policy for Quality in Healthcare
Bridging Silos, Accelerating Improvements
The MOH is consisted of two major components- the technical programmes and the
administrative arm. There are six technical programmes— Public Health (which
includes public health and primary health care), Medical (hospitals and specialist
care), Oral Health, Pharmaceutical Services, Food Safety and Quality, and Research &
Technical Support—each headed by either a Deputy Director General (DDG) or Senior
Principal Director, who reports to the Director General of Health. In addition, various
administrative arms of the ministry, including Management and Finance, are led by
respective Deputy Secretary Generals and report directly to the Secretary General (6).
The public healthcare system is largely funded by the government and financed mainly
from public tax revenue. On the other hand, healthcare services delivered by the private
sector are funded primarily through private health insurance, out of pocket payment
by consumers, and also by non-profit institutions. The public health sector provides
approximately 75.5 % of inpatient care and 64.3% of ambulatory care while the private
sector provides the remaining inpatient and ambulatory healthcare services (7).
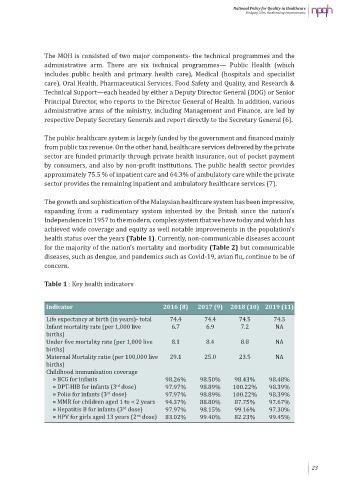
The growth and sophistication of the Malaysian healthcare system has been impressive,
expanding from a rudimentary system inherited by the British since the nation’s
Independence in 1957 to the modern, complex system that we have today and which has
achieved wide coverage and equity as well notable improvements in the population’s
health status over the years (Table 1). Currently, non-communicable diseases account
for the majority of the nation’s mortality and morbidity (Table 2) but communicable
diseases, such as dengue, and pandemics such as Covid-19, avian flu, continue to be of
concern.
Table 1 : Key health indicators
Indicator 2016 (8) 2017 (9) 2018 (10) 2019 (11)
Life expectancy at birth (in years)- total 74.4 74.4 74.5 74.5
Infant mortality rate (per 1,000 live 6.7 6.9 7.2 NA
births)
Under five mortality rate (per 1,000 live 8.1 8.4 8.8 NA
births)
Maternal Mortality ratio (per 100,000 live 29.1 25.0 23.5 NA
births)
Childhood immunisation coverage
» BCG for infants 98.26% 98.50% 98.43% 98.48%
rd
» DPT-HIB for infants (3 dose) 97.97% 98.89% 100.22% 98.39%
rd
» Polio for infants (3 dose) 97.97% 98.89% 100.22% 98.39%
» MMR for children aged 1 to < 2 years 94.37% 88.80% 87.75% 97.67%
rd
» Hepatitis B for infants (3 dose) 97.97% 98.15% 99.16% 97.30%
nd
» HPV for girls aged 13 years (2 dose) 83.02% 99.40% 82.23% 99.45%
23