Page 23 - Recommendations-for-biostatisticians-in-managing-and-conducting-medical-research-consultations
P. 23
4.2 Conceptual framework
Conceptual framework (CF) is a visualization technique to portray the association of the
independent variables and moderator variables with the dependent variable. It should not
be confused with a theoretical framework (TF). Although TF may look similar to CF,
however the key variables of TF are based on theory where the relationship or association
has already been proven valid. Unlike TF, CF is a hypothesized relationship or association
that has yet to be tested by research (Rocco and Plakhotnik 2009). This explains why CF is
a visualization technique commonly used by students when they are writing up their
dissertations. Occasionally, this technique is also being applied in the preparation of
scientific manuscripts.
Previously, TEV provides a broader picture of a disease event among patients with a
similar disease while CF describes a specific hypothesis intended to be tested within a TEV
model. TEV has previously been used to describe the sequence of events that commonly
occur in the T2DM patients from an early stage until all the clinical outcomes have been
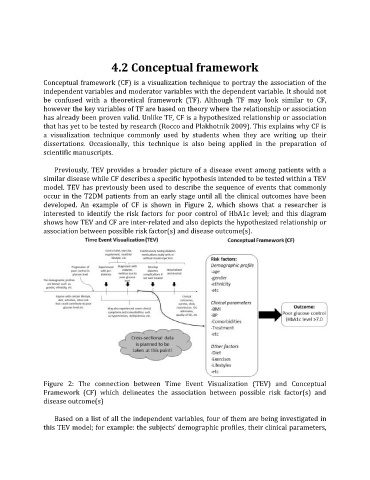
developed. An example of CF is shown in Figure 2, which shows that a researcher is
interested to identify the risk factors for poor control of HbA1c level; and this diagram
shows how TEV and CF are inter-related and also depicts the hypothesized relationship or
association between possible risk factor(s) and disease outcome(s).
Figure 2: The connection between Time Event Visualization (TEV) and Conceptual
Framework (CF) which delineates the association between possible risk factor(s) and
disease outcome(s)
Based on a list of all the independent variables, four of them are being investigated in
this TEV model; for example: the subjects’ demographic profiles, their clinical parameters,