Page 79 - Living-on-the-frontline-of-COVID-19-in-MCO-and-CMCO
P. 79
Evaluation of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki
Disease
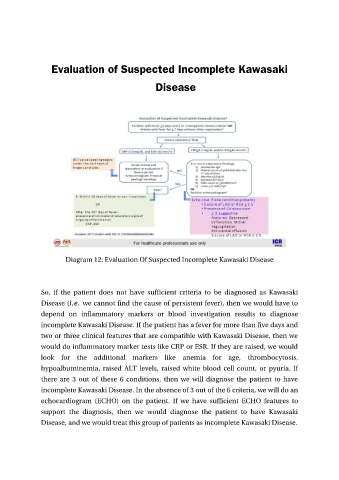
Diagram 12: Evaluation Of Suspected Incomplete Kawasaki Disease
So, if the patient does not have sufficient criteria to be diagnosed as Kawasaki
Disease (i.e. we cannot find the cause of persistent fever), then we would have to
depend on inflammatory markers or blood investigation results to diagnose
incomplete Kawasaki Disease. If the patient has a fever for more than five days and
two or three clinical features that are compatible with Kawasaki Disease, then we
would do inflammatory marker tests like CRP or ESR. If they are raised, we would
look for the additional markers like anemia for age, thrombocytosis,
hypoalbuminemia, raised ALT levels, raised white blood cell count, or pyuria. If
there are 3 out of these 6 conditions, then we will diagnose the patient to have
incomplete Kawasaki Disease. In the absence of 3 out of the 6 criteria, we will do an
echocardiogram (ECHO) on the patient. If we have sufficient ECHO features to
support the diagnosis, then we would diagnose the patient to have Kawasaki
Disease, and we would treat this group of patients as incomplete Kawasaki Disease.